Understanding Financing Options

Choosing the right financing method for your solar panel installation is crucial, as it significantly impacts your upfront costs, monthly payments, and overall long-term expenses. Understanding the nuances of each option will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your financial situation and long-term goals. This section will explore the three primary financing options: loans, leases, and Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs).
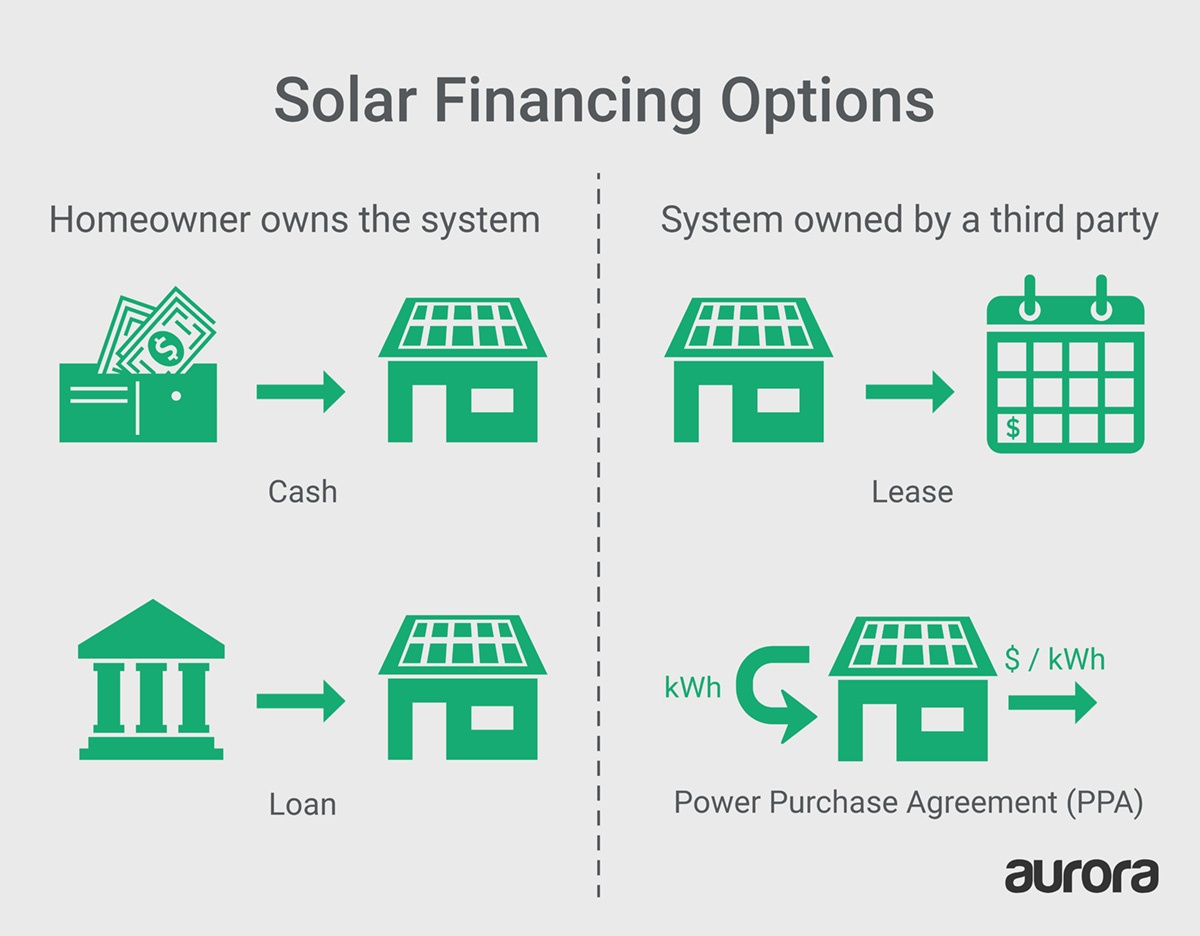
Solar Loan Financing
A solar loan is essentially a traditional loan specifically for financing solar panel installations. You borrow a lump sum from a lender, typically a bank or credit union, to cover the total cost of the system. You then repay the loan with fixed monthly payments over an agreed-upon term (often 10-25 years). Interest rates vary depending on your credit score and the lender.
Advantages of solar loans include potential tax credits and deductions, full ownership of the system from the outset, and the ability to build equity in your home. Disadvantages include higher upfront costs compared to leases and PPAs, and the risk of higher overall costs if interest rates are high. The total cost of ownership over 20 years will depend heavily on the interest rate. For example, a $20,000 loan at 5% interest over 15 years will cost significantly more than the same loan at 3% interest.
Solar Lease Financing
With a solar lease, you don’t own the solar panels; instead, you pay a monthly fee to the solar leasing company for the electricity generated by the system installed on your roof. This eliminates the upfront costs associated with purchasing and installing the panels.
The advantage of a solar lease is its low or no upfront cost. The disadvantage is that you don’t own the system, and you don’t receive any tax credits or incentives associated with ownership. Also, monthly payments may be higher than loan payments over the long term, resulting in a higher total cost of ownership. Lease agreements typically run for 20 years or more, meaning you’ll be making payments for an extended period.
Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) Financing
A Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) is similar to a solar lease in that you don’t own the solar panels. However, instead of paying a fixed monthly fee, you pay for the electricity generated by the system at a pre-agreed-upon rate, usually lower than your current utility rate. The solar company owns, operates, and maintains the system.
The advantages of a PPA include no upfront costs and potentially lower electricity bills. The disadvantages are that you don’t own the system, and the long-term savings may be less than with a loan, depending on electricity price fluctuations and the PPA’s terms. Furthermore, you are locked into a contract for a specific duration, and you might not be able to sell your home as easily as with owned panels.
Comparison of Financing Options
The following table summarizes the key features of each financing option:
| Financing Type | Upfront Cost | Monthly Payment | Ownership |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Loan | High | Variable (depends on interest rate and loan term) | You own the system |
| Solar Lease | Low or None | Fixed (typically higher than loan payments over the long term) | Solar company owns the system |
| Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) | None | Variable (based on electricity consumption and pre-agreed rate) | Solar company owns the system |
Assessing Installer Reputation and Customer Service

Choosing a solar installer involves more than just comparing prices; it’s crucial to assess their reputation and commitment to customer service. A reputable installer will not only deliver a quality installation but also provide ongoing support and address any concerns promptly. Neglecting this aspect can lead to costly problems down the line.
Online reviews and testimonials offer a valuable glimpse into a solar installer’s performance and customer relations. However, it’s important to approach this information critically to avoid misleading or manipulated feedback.
Analyzing Online Reviews and Testimonials
Online platforms like Google Reviews, Yelp, and the Better Business Bureau (BBB) host numerous reviews from past clients. These reviews often provide insights into the installer’s professionalism, responsiveness, communication skills, and the overall quality of their work. Look for consistent patterns in positive and negative feedback. A high volume of positive reviews with detailed descriptions of positive experiences is a good sign. Conversely, a significant number of negative reviews highlighting similar issues should raise concerns.
Verifying the Authenticity of Online Reviews
Not all online reviews are genuine. Some installers might attempt to inflate their ratings through fake reviews, while competitors might post negative reviews to damage their reputation. To verify authenticity, consider the following:
* Check review dates and patterns: A sudden surge in positive reviews might indicate manipulation. Look for reviews spanning a longer period to get a more balanced perspective.
* Examine review details: Generic, overly positive reviews without specific details should be treated with skepticism. Authentic reviews often include specific examples and anecdotes.
* Cross-reference reviews across multiple platforms: If an installer has overwhelmingly positive reviews on one platform but significantly negative reviews on another, it warrants further investigation.
* Look for responses to reviews: Reputable installers actively engage with both positive and negative reviews, addressing concerns and showing a commitment to customer satisfaction.
Contacting Previous Clients
Directly contacting previous clients offers the most reliable way to assess an installer’s reputation. You can find contact information through online reviews or by requesting references from the installer. When contacting previous clients, ask specific questions about their experience, such as:
* The installer’s punctuality and professionalism.
* The quality of the installation and any unexpected issues.
* The installer’s responsiveness to questions and concerns before, during, and after the installation.
* Their overall satisfaction with the service received.
Remember to be polite and respectful when contacting previous clients.
Methods for Assessing Installer Reputation
| Method | Reliability | Effort Required | Potential Bias |
|---|---|---|---|
| Online Reviews (Google, Yelp, BBB) | Moderate (potential for fake reviews) | Low | Potential for both positive and negative bias |
| Contacting Previous Clients | High | High | Minimal bias, assuming genuine responses |
| Checking Licensing and Insurance | High | Low to Moderate | Minimal bias; objective verification |
| Checking with Local Authorities and Industry Associations | High | Moderate | Minimal bias; objective verification |
Examining the Solar Proposal and Contract: How To Choose A Solar Installer To Finance
A comprehensive solar proposal and a meticulously reviewed contract are crucial for a successful solar installation. These documents Artikel the entire project, from system design to payment schedules and warranties. Carefully examining both will protect your investment and ensure you receive the system you expect.
How to choose a solar installer to finance – Understanding the details within the proposal and contract is vital to avoid unexpected costs and ensure a smooth installation process. This involves scrutinizing the specifics of the system, the equipment used, the warranties offered, and the payment terms laid out in the contract.
Solar Proposal Components
A detailed solar proposal should include several key components. System size, typically measured in kilowatts (kW), determines the amount of energy your system will generate. This is based on your energy consumption and roof suitability. Equipment specifications should list the specific panels, inverters, and racking systems to be used, including their manufacturer, model numbers, and efficiency ratings. Warranties are crucial; they should cover the performance of the panels and other equipment for a specified period, typically 25 years for panels and 10-15 years for inverters. The proposal should also clearly Artikel the installation timeline, payment schedule, and any permits or inspections required.
Solar Contract Review
Thoroughly reviewing the solar installation contract is a critical step. Begin by carefully reading each clause, paying close attention to hidden fees, such as permitting fees, interconnection charges, or site assessment costs. Scrutinize the payment schedule, ensuring it aligns with the installation timeline and that progress payments are tied to specific milestones. Understand the cancellation policy and any penalties for early termination. Verify that the contract accurately reflects the system specifications detailed in the proposal. Look for clauses that address potential disputes and how they will be resolved. Finally, ensure the contract clearly defines responsibilities for both you and the installer.
Warranty Comparison
Solar panel and inverter warranties vary significantly between manufacturers and installers. Common warranties include performance warranties, which guarantee a certain level of energy production over time, and product warranties, which cover defects in materials and workmanship. Some installers offer extended warranties or performance guarantees for added peace of mind. It’s essential to compare the length, terms, and conditions of warranties from different installers to make an informed decision. For example, one installer might offer a 25-year panel warranty with a 10% performance guarantee, while another offers a 25-year warranty with a 90% performance guarantee. The difference in performance guarantees can significantly impact the system’s long-term energy output.
Critical Contract Aspects
| Contract Section | Key Information | What to Look For | Potential Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| System Specifications | Panel model, inverter model, system size (kW) | Accuracy and match with proposal | Discrepancies between proposal and contract |
| Payment Schedule | Down payment, progress payments, final payment | Clear milestones tied to payments | Unclear payment terms, excessive upfront costs |
| Warranties | Panel warranty, inverter warranty, workmanship warranty | Length of warranty, terms and conditions | Short warranty periods, limited coverage |
| Dispute Resolution | Process for handling complaints or disagreements | Clear and fair process | Lack of clear dispute resolution mechanism |
| Cancellation Policy | Conditions for cancellation, potential penalties | Reasonable terms and conditions | Unreasonable penalties for cancellation |
| Permitting and Inspections | Responsibilities for obtaining permits and inspections | Clear allocation of responsibilities | Unclear responsibility for permitting delays or costs |
Understanding Permitting and Installation Process
Successfully navigating the permitting and installation process is crucial for a smooth solar energy transition. This involves understanding the necessary steps, timelines, and communication strategies to ensure a timely and compliant installation. Clear communication with your installer is key throughout this phase.
The permitting process varies by location, but generally involves submitting detailed plans and specifications to your local authority having jurisdiction (AHJ). This usually includes the building department and potentially the utility company. The AHJ will review the plans to ensure they meet all safety and building codes. Once approved, you’ll receive the necessary permits to proceed with installation. The timeline for obtaining permits can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the complexity of the project and the efficiency of your local AHJ. Delays are common, so factoring in potential delays in your project timeline is advisable.
Permitting Requirements and Procedures
Securing the necessary permits is a critical first step. This typically involves submitting a detailed application, including site plans, system specifications, and electrical diagrams, to your local building department and potentially the utility company. The specific requirements will vary depending on your location and the size of the system. Expect to provide information about your property, the proposed solar panel layout, and the electrical connection points. Thorough preparation and accurate documentation will expedite the review process. Following up regularly with the AHJ can help to identify and resolve any issues quickly. After approval, you’ll receive the necessary permits allowing the installer to commence work.
Typical Timeline for Solar Installation
A typical solar installation project unfolds in several stages, each with its own timeframe. While exact timelines vary based on factors like project size, permit approvals, and weather conditions, a general Artikel helps manage expectations. A small residential installation might take 4-6 weeks, while larger commercial projects can extend to several months. Consider these phases: Initial consultation and site assessment (1-2 weeks); Permitting (2-8 weeks); Equipment ordering and delivery (1-4 weeks); Installation (1-2 weeks); Inspections and final connection (1-2 weeks). Unexpected delays, such as material shortages or adverse weather, can impact the overall timeline.
Effective Communication with the Installer, How to choose a solar installer to finance
Maintaining open and consistent communication with your solar installer is vital throughout the entire process. Regular updates, whether through email, phone calls, or in-person meetings, help keep you informed of the project’s progress and address any concerns promptly. Establish a clear communication plan at the outset, defining preferred methods and frequency of contact. Document all communication, including emails, meeting notes, and any agreements made. Don’t hesitate to ask questions or express concerns. A responsive and communicative installer will build your confidence and ensure a positive experience.
Solar Installation Project Timeline
| Stage | Duration (Estimated) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Consultation & Site Assessment | 1-2 weeks | Installer visits your property, assesses suitability, and discusses system design. |
| Permitting Process | 2-8 weeks | Application submission, review by AHJ, and permit issuance. |
| Equipment Procurement & Delivery | 1-4 weeks | Ordering and delivery of solar panels, inverters, and other components. |
| Installation | 1-2 weeks | Physical installation of solar panels, racking, inverters, and electrical connections. |
| Inspections & Final Connection | 1-2 weeks | Inspections by AHJ and utility company, followed by final system activation. |

Tim Redaksi